





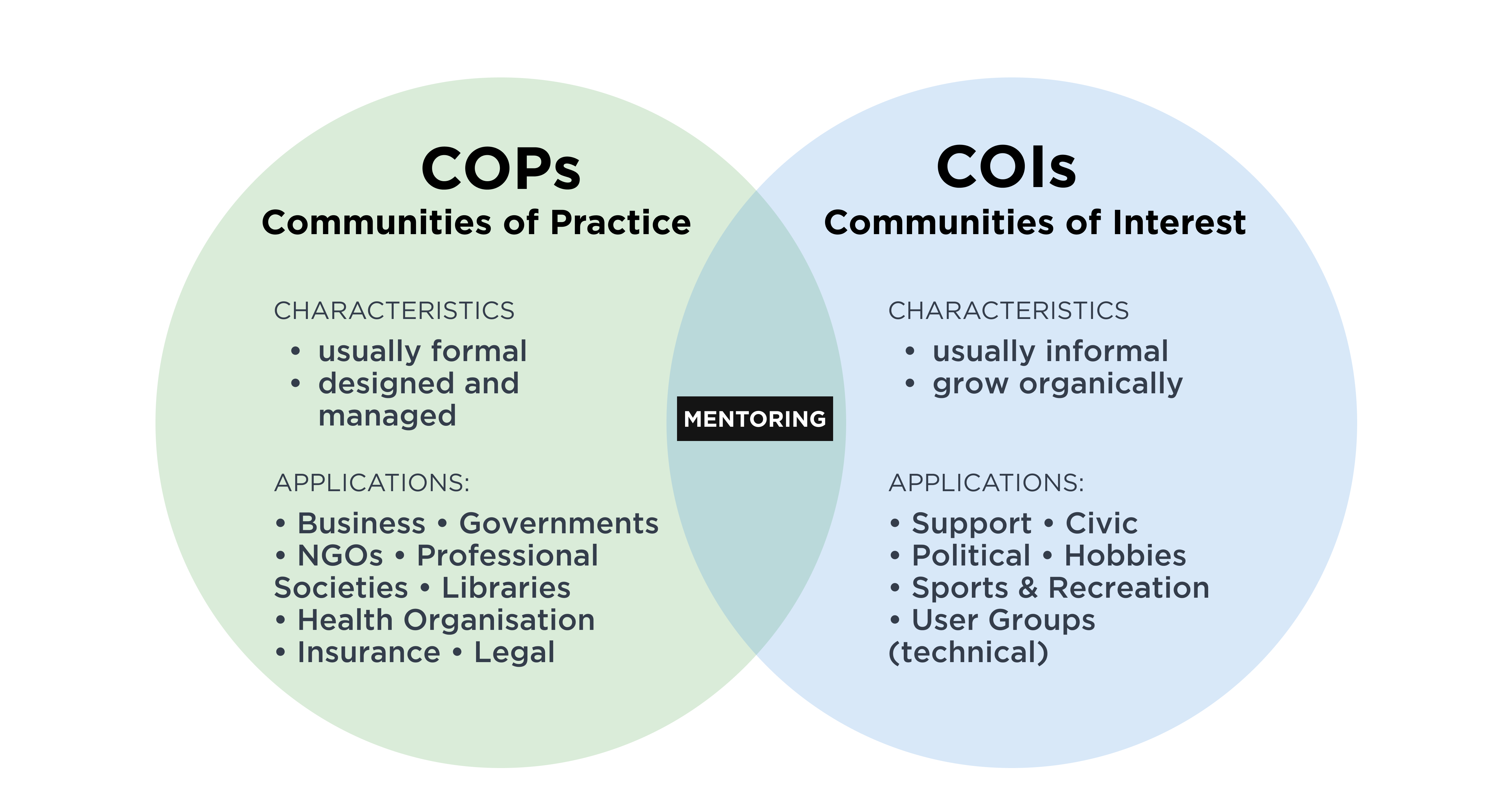
Communities of Practice (CoPs) and Communities of Interest (CoIs) involve people who come together based on shared interests or goals. However, the distinct differences between the two concepts are essential to understand. These differences, particularly in purpose, structure, and outcomes, set them apart and make them valuable in their own ways.
At the intersection between Communities of Practice and Communities of Interest, individuals progress from merely having an interest in a topic to becoming active practitioners. This progression involves deepening engagement, continuous learning, and developing new skills through the collective environment of CoPs. The collaboration within this intersection enriches the community with fresh expertise.
CoPs are centered around the shared practice and development of expertise in a specific domain. Members engage in collective learning through regular interaction and collaboration, fostering a sense of belonging and support to improve their skills and knowledge in a particular practice area. For example, a CoP of software developers might focus on enhancing coding practices, sharing new technologies, and solving technical challenges collaboratively.
The primary purpose of CoIs is to unite individuals with a common interest to share information, discuss ideas, and network. They typically come from all walks of life and tend not to focus on a specific professional practice within the area of interest. An example of a CoI could be a group of citizens interested in renewable energy who meet to discuss current affairs and policy impacts and share their opinions.
Typically, they have a more structured approach to membership and interaction. Members are usually practitioners or professionals who actively engage in their domain of practice. The community is often characterized by regular meetings, both formal and informal, where members collaborate on real-world problems, share experiences, and develop new practices. Membership is based on active participation and contribution to the community’s goals and may require a financial commitment.
CoIs are generally more open and less structured than CoPs. Membership is often informal and can include anyone interested in the topic, regardless of their level of expertise or active involvement. This democratic nature empowers individuals to contribute to a diverse community. CoIs may have occasional meetings or online forums where members share information and engage in discussions.
Members benefit from enhanced skills, more profound knowledge, and problem-solving capabilities, leading to personal growth and professional development. CoPs contribute to organizational learning and innovation by creating a repository of shared practices and solutions that can be leveraged across the organization. The impact of CoPs is often seen in increased performance, efficiency, and the ability to adapt to new challenges within the practice area.
The primary outcome of CoIs is the dissemination of information and the exchange of ideas. Members benefit from staying informed about developments in their area of interest and expanding their network of contacts. While CoIs can inspire new ideas and raise awareness about important topics, they do not necessarily lead to the development of shared practices or direct improvements in professional practice. CoIs increase awareness, drive advocacy, and create networking opportunities.
The following table concisely compares Communities of Practice and Communities of Interest, highlighting their key differences in purpose and focus, structure and membership, and outcomes and impact.
A prime example of a successfully used Community of Practice is Intel's DevMesh, built on platformOS. Intel leveraged the power of CoPs to enhance collaboration among its engineers and developers by creating a structured environment for knowledge sharing and innovation. Intel's DevMesh helps improve problem-solving capabilities, drive constant improvement, and encourage a learning culture within the organization. This initiative greatly enhances Intel's operational efficiencies and contributes to its position as a leader in the technology industry. For more details, you can read the full success story here.
By understanding the unique roles of Communities of Practice and Communities of Interest, you can use this knowledge to achieve desired outcomes. CoPs focus on developing and improving practice within a specific domain through regular collaboration and shared learning. CoIs, on the other hand, unite individuals with a common interest to share information and ideas. By understanding these differences, you can effectively leverage each type of community to enhance your professional and personal contexts.
Our totally customizable community solution can give you complete control to innovate at your own scale.